Articles and Trivia
Write an articleSemiconductor Devices
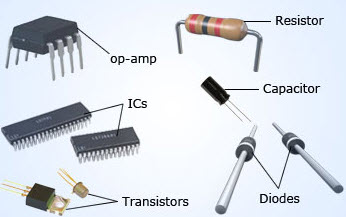
Semiconductor devices play a crucial role in modern electronics due to their unique properties. These devices are electronic components that rely on semiconductor materials for their functionality. A semiconductor material sits between conductors, like copper, and insulators, such as glass, in terms of electrical conductivity. The most common semiconductor materials include silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide.
Semiconductor devices come in various types, with examples like bipolar transistors, diodes, field-effect transistors, silicon-controlled rectifiers, and integrated circuits. Discrete semiconductors are single devices with individual functions, while integrated circuits incorporate multiple functional elements onto one chip. These devices are known for their compactness, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Bipolar transistors, diodes, and field-effect transistors are among the most common semiconductor devices in use. They are utilized in numerous products and components, forming the backbone of many electronic systems. These semiconductor devices are essential in various industries, including telecommunications, computing, automotive, and power electronics.
Semiconductor devices have largely replaced vacuum tubes in electronic applications due to their smaller size, lower power consumption, and enhanced reliability. Integrated circuits, which contain complex arrangements of semiconductor components on a single chip, have revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling the creation of powerful and compact electronic devices.
In conclusion, semiconductor devices have significantly impacted modern technology, providing the foundation for countless electronic advancements. Their versatility, efficiency, and reliability have made them indispensable components in the ever-evolving world of electronics and technology.


